Welcome to EMEP¶
This guide gives a brief documentation of the EMEP/MSC-W model version rv4.10. It is intended primarily as a guide on how to run the model, and to help users wishing to understand or change the model in terms of domains, outputs, chemistry, etc.
The main documentation for the EMEP/MSC-W model is an article published in Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics in 2012. This article will be referred to as Simpson et al. (2012) in this manual.
Simpson, D., Benedictow, A., Berge, H., Bergström, R., Emberson, L.D., Fagerli, H., Flechard, C.R., Hayman, G.D., Gauss, M., Jonson, J.E., Jenkin, M.W., Nyíri, Á, Richter, C., Semeena, V.S, Tsyro, S., Tuovinen, J.-P., Valdebenito, Á., and Wind, P.: The EMEP MSC-W chemical transport model – technical description. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 12, 7825-7865, 2012.
http://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/12/7825/2012/acp-12-7825-2012.html
The model source code is available from the Open Source EMEP/MSC-W model github page:
https://github.com/metno/emep-ctm
Licenses and Caveats¶
The EMEP code is provided under the GNU General Public License version 3 (http://fsf.org and/or http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.html).
Each code module is prefaced with something like:
! <EXAMPLE_CODE.f90 - A component of the EMEP MSC-W Eulerian
! Chemical transport Model>
!*******************************************************************!
!*
!* Copyright (C) 2007-2016 met.no
!*
!* Contact information:
!* Norwegian Meteorological Institute
!* Box 43 Blindern
!* 0313 OSLO
!* NORWAY
!* email: emep.mscw@met.no
!*
!* This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
!* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
!* the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
!* (at your option) any later version.
!*
!* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
!* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
!* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
!* GNU General Public License for more details.
!*
!* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
!* along with this program. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
!*******************************************************************!
And a copy of the license file, gpl.txt, is provided with the model code source files.
It is important to note that the code is provided “as it is”, and EMEP/MSC-W has very limited resources with which to support usage of the code.
Computer Information¶
To compile the EMEP/MSC-W model you need:
- Fortran 95 compiler
- NetCDF Library (> 4.1.3)
- MPI Library (> 1.0)
It is necessary to compile with double precision real (8 bytes real).
The program has been used on computers ranging from a Linux laptop to
supercomputers (Itanium2 cluster, Intel Xeon cluster, Cray XT4, IBM
power5+). It is compatible with all compilers tested so far: Intel, PGI,
gfortran, XL Fortran. A Makefile is included, the path to NetCDF (INCL
and LLIB) have to be adapted to your machine, and the Fortran compiler
(F90) and flags (F90FLAGS) to the compiler you are using.
The code has been tested with 1 to 1024 CPUs, and scales well (for large grids). If only one CPU is used 1-2 GB memory is required. If more than one, for example 64 CPUs are used, 200 MB of memory per CPU is enough (in the case of a 132 X 159 grid size). For runs on more than 32 CPUs, a fast interconnect is recommended (infiniband for example), for smaller runs, gigabit Ethernet is sufficient. It takes ~5 hours on 64*Xeon X5355 (2.66GHz) for 1 year simulation.
When downloading input data in order to do a “base run” please make sure that there are 35 Gb disc space available, especially due to large meteorology input files. The model can be run for shorter periods, users can download meteorology for only the period they are interested in, plus one day.
Getting Started¶
It is recommended to read all the chapters of this EMEP/MSC-W model User Guide before you start downloading anything from the EMEP/MSC-W Open Source website.
This is what you need to do before you can do a “base run” with the EMEP/MSC-W model:
- Read the EMEP/MSC-W model User Guide
- Download input data,
description and downloading instructions in
ch-inputfiles. - Download the EMEP/MSC-W model source code,
description and downloading instructions
sec-modelcode. - Follow the instructions for “Submitting a Run” description in
ch-submitarun. - Download some model results for comparison,
description in and downloading instructions
ch-output.
Model code¶
The latest release Open Source of the EMEP/MSC-W model is version rv4_10. This and previous releases can be found on the releases section of the EMEP/MSC-W Open Source github page.
Although the source code is available for download as a single compressed file on the release page, the preferred retrieval method is via the catalog tool as follows:
# download the catalog tool
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metno/emep-ctm/master/tools/catalog.py
# make it executable and run it
chmod +x catalog.py
# download the source code for rv4_10 release
catalog.py -R rv4_10 --source
The model source code, makefiles, and a copy of the license file
will be placed under the directory EMEP_MSC-W_model.rv4.10.OpenSource/source/.
An overview of the files is given in Table 1.
| Type | Filename |
|---|---|
| modules files | *.f90 |
| include files | *.inc |
| namelist | config_emep.nml |
| makefiles | Makefile and Makefile.SRCS |
| dependency file | dependencies |
| a copy of the license | gpl.txt |
In addition there is a run script called modrun.sh, which will be
placed in the EMEP_MSC-W_model.rv4.10.OpenSource directory. The run script,
modrun.sh, can easily be modified to work on your computer system.
This script is described in detail in ch-submitarun.
Model grid¶
The current EMEP model version, and the provided gridded input data, have a horizontal resolution of \(50\times 50 km^2\) (at \(60^\circ N\)) and are defined on a polar stereographic projection with 20 sigma levels vertically. The model is very flexible with regard to the horizontal resolution, in that it readily makes use of meteorological data provided with the model. The vertical resolution is currently still restricted to the fixed 20 layer system. The physical description is given in detail in Chapter 2 of the EMEP Status Report 1/2003 Part I (Simpson et al., 2003).
In 2008 the EMEP domain was extended eastwards in order to include the
EECCA countries in the EMEP model grid, see Figure 1.
To distinguish the new grid from the old EMEP grid, the new grid is called
EECCA in this text and in the config_emep.nml.
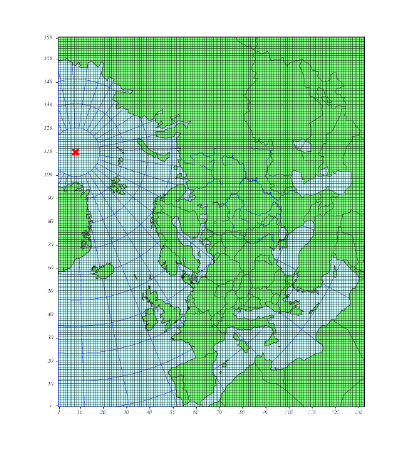
Figure 1 The extended EMEP grid covering EECCA area with \(132\times 159\) gridpoints on \(50\times 50 km^2\) resolution defined on a polar stereographic projection.